Menu
Math Lesson 14.5.3 - Finding the Midpoint of a Line Segment
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Math lesson on Finding the Midpoint of a Line Segment, this is the third lesson of our suite of math lessons covering the topic of Line Segments, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional Math learning resources below this lesson.
Finding the Midpoint of a Line Segment
The midpoint of a line segment is a point in that segment which has the same distance from both endpoints. In other words, the midpoint M of the segment AB is halfway of the straight path that brings from A to B or from B to A.
When trying to find the midpoint of a line segment AB, it is better to make it express in two different equations, according to the two main directions. Look at the figure below.
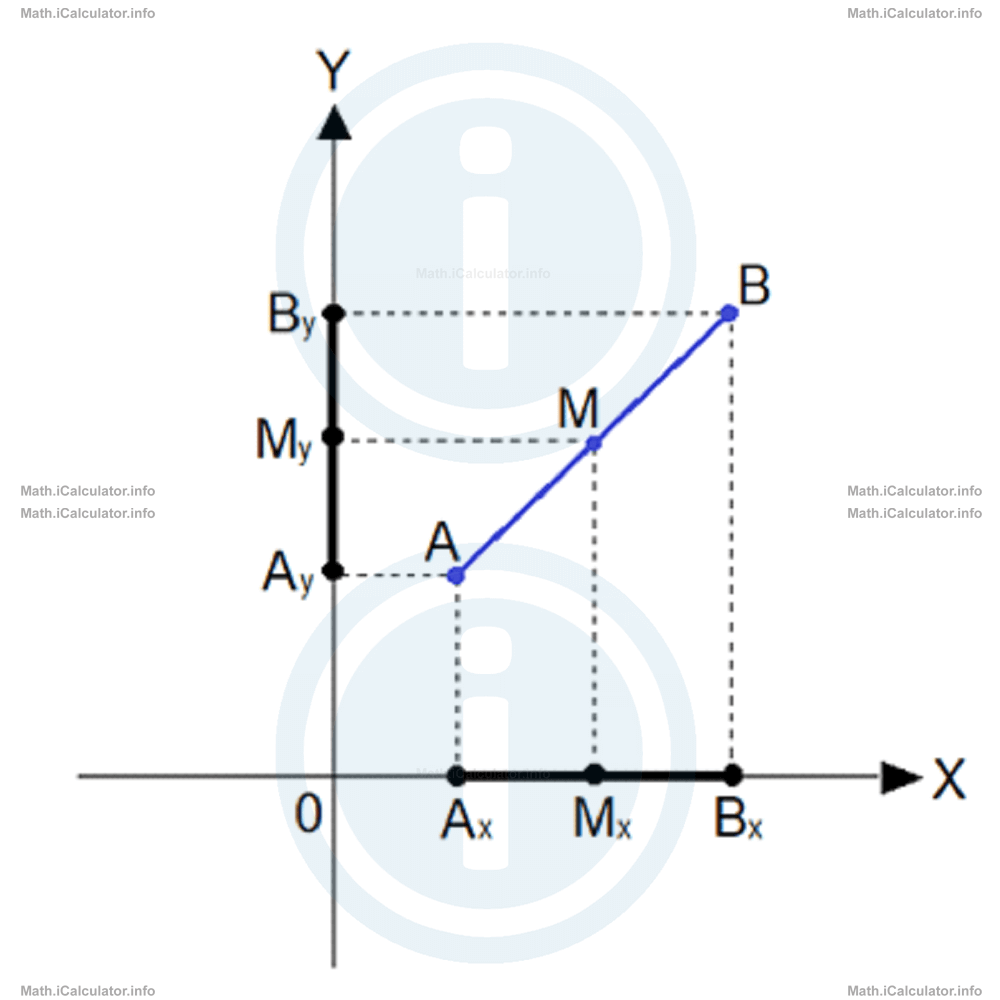
From the figure, it is clear that if point M is a midpoint of the segment AB, so must be Mx for ABx and My,/sub> for ABy as well. If the coordinates of points A and B are known, then we use the concept of arithmetic mean to calculate the x-and y-coordinates of the midpoint. (We will explain later on in this course the arithmetic mean concept but for now, it is sufficient to say that arithmetic mean is the usual average you find every time you have a set of different numbers and want to know what number can substitute all values in the data set to give the same result when added. For example, when you want to know the average score of two exams, you add the scores and divide the sum by 2. In this way, you find the arithmetic mean of the two exam scores - a number that you can use to estimate your level of understanding of the given subject.)
From all said above, we conclude that we must add the coordinates of points A and B for each direction separately and divide by 2 the sums obtained. In this way, we obtain the x- and y-coordinates of the midpoint M. In symbols, we have
= xA + xB/2
and
= yA + yB/2
where A is the leftmost point of the two. We can also express the two endpoints by the indices (1) and (2) respectively, as subscripts. In this way, we obtain the general form of the two midpoint formulas above:
= x1 + x2/2
and
= y1 + y2/2
Example 3
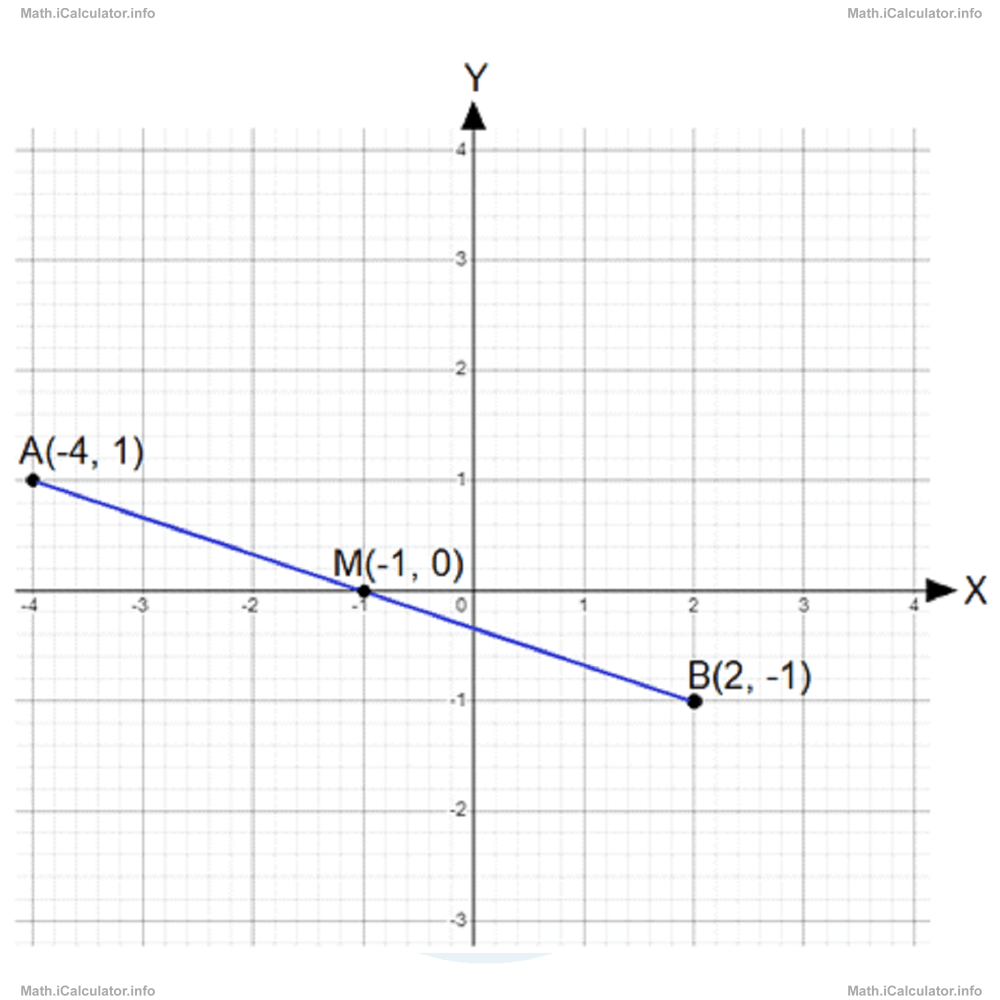
Calculate the coordinates of the midpoint M for the segment AB if the coordinates of the endpoints A and B are A(-4, 1) and B(2, -1).
Solution 3
We have xA = -4, xB = 2, yA = 1 and yB = -1. From the two midpoint formulas
= xA + xB/2
and
= yA + yB/2
we obtain for the coordinates of the midpoint M after substituting the given numbers:
= xA + xB/2
= -4 + 2/2
= -2/2
= -1
and
= yA + yB/2
= 1 + (-1)/n2
= 0/2
= 0
Therefore, the midpoint M of the segment AB is M(-1, 0). Look at the figure below for confirmation.
What is the importance of the midpoint of a segment? Well, there are several reasons why knowing the coordinates of the midpoint of a segment is a good thing, where the most important is to check whether a given graph is linear or not. For example, we may face a marginal part of a parabola produced by a quadratic graph that at the first sight looks linear but it isn't instead. For example, in the figure below,
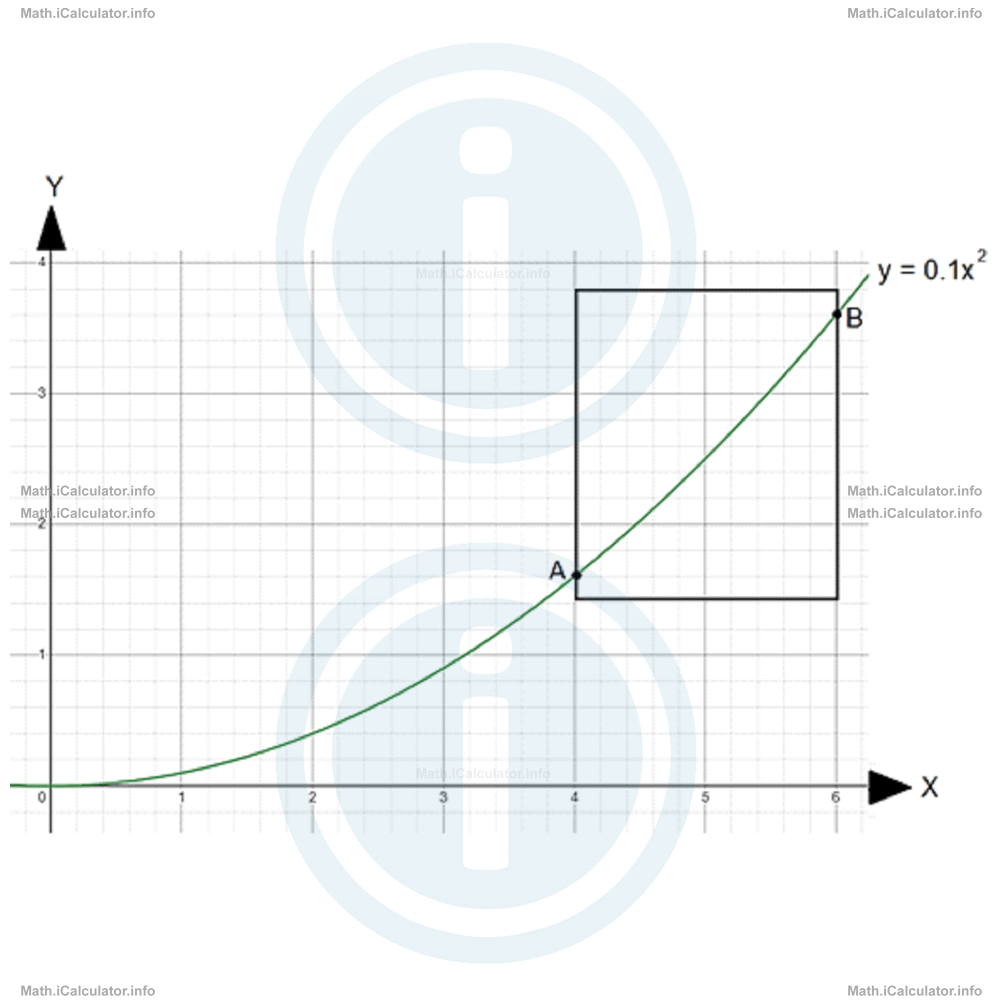
the part of the graph inside the square looks very close to a straight line. Thus, we can find the coordinates of the midpoint of the supposed segment AB that extends from the leftmost part of the highlighted graph A(4, 1.6) to the rightmost one B(6, 3.6). Thus, using the equations of the midpoint M of a line segment
= xA + xB/2
and
= yA + yB/2
we obtain after substituting the known values
= 4 + 6/2
= 10/2
= 5
and
= 1.6 + 3.6/2
= 5.2/2
= 2.6
However, we see that the supposed midpoint M(5, 2.6) is not on the graph but slightly above it, as shown in the figure below.
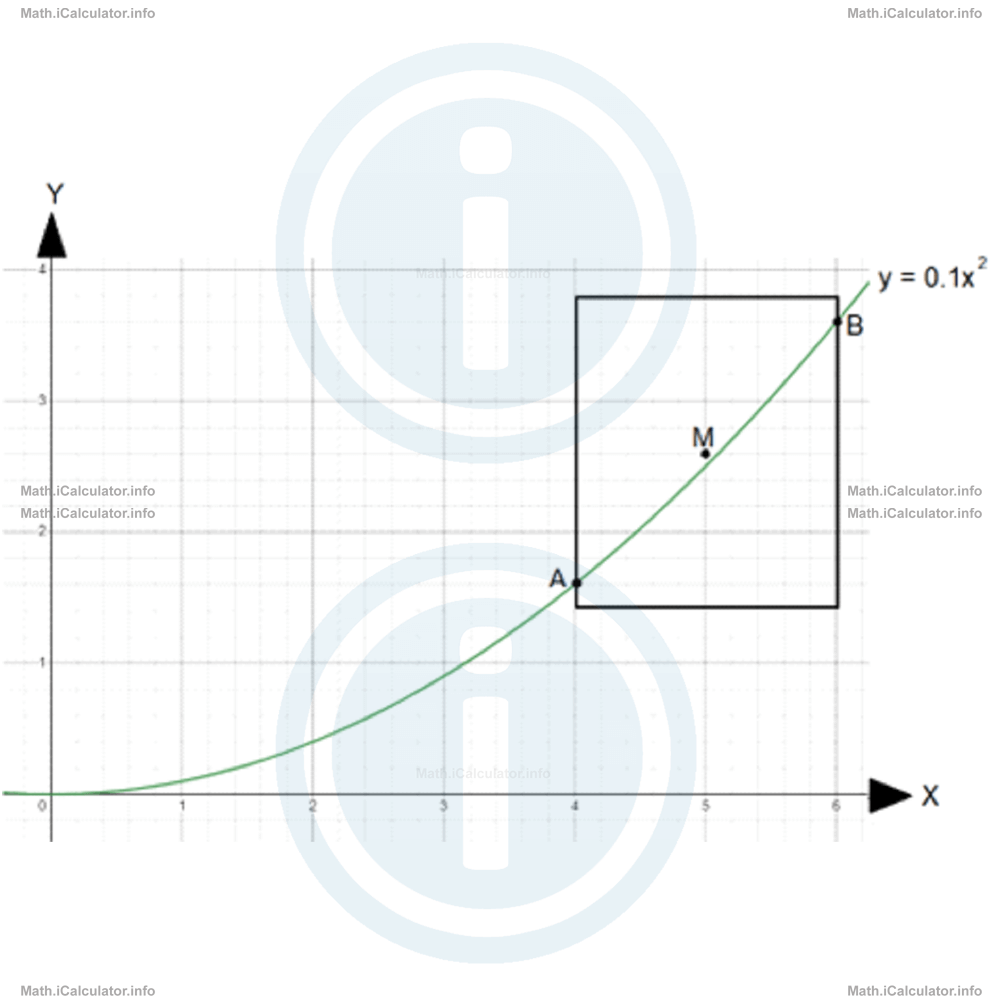
This means M is not a midpoint of AB and consequently, AB is not a line segment. This means the graph is not linear.
More Line Segments Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Finding the Midpoint of a Line Segment" math lesson? People who liked the "Line Segments lesson found the following resources useful:
- Midpoint Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this midpoint (see below)
- Linear Graphs Math tutorial: Line Segments. Read the Line Segments math tutorial and build your math knowledge of Linear Graphs
- Linear Graphs Revision Notes: Line Segments. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the math tutorial for Line Segments
- Linear Graphs Practice Questions: Line Segments. Test and improve your knowledge of Line Segments with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Linear Graphs questions with our excellent Linear Graphs calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Linear Graphs Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning linear graphs - read our next math tutorial: Linear Graphs
Help others Learning Math just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Math tutorial "Line Segments" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this math tutorial (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this math learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of math and other disciplines.