Menu
Math Lesson 9.3.5 - Solving by Proof
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Math lesson on Solving by Proof, this is the fifth lesson of our suite of math lessons covering the topic of Identities, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional Math learning resources below this lesson.
Solving by Proof
This is a very powerful method used in mathematics to solve questions of a high level of difficulty. In the previous example, we used this method when proving that the equation given was an identity. Proof is closely related to identities as in many cases, we have to confirm that a relationship is always true.
To solve an exercise that requires proving that something is always true, we start from a known fact; then, step - by - step we move towards the final solution (proof). Let's clarify this point through an example.
Example 3
Prove that the sum of three consecutive integers is divisible by 3.
Solution 3
Let's express the smallest number by x. Thus, the next two numbers will be x + 1 and x + 2 respectively. Their sum S expressed in terms of x is
= x + x + 1 + x + 2
= 3x + 3
= 3(x + 1)
From the factorised form obtained in the last transformation, it is clear that one of the factors of the sum of three consecutive numbers is 3. Therefore, their sum will always be divisible by 3 regardless of the numbers taken into consideration.
Solving by proof is widely applied in geometry as well. Let's consider an example where proof helps us find a relationship that is always true in geometry.
Example 4
Prove that the sum of the measures m of interior angles in a triangle is always 180°. For this, the following info is necessary:
"When a line intersects two other parallel lines, it produces eight angles in total that are 4 by 4 equal. Two of such equal angles known as 'alternate interior angles' expressed in the figure below as x and y (x = y), are formed at the inner corners of the 'Z' - like symbol produced by the intersection of the three lines".
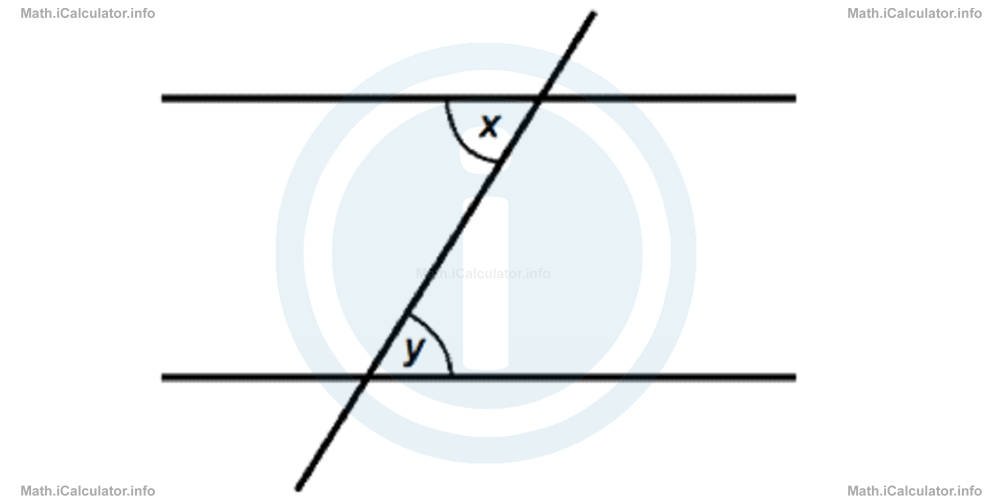
Other useful info: The measure of a right angle is 90°, that of a straight angle is 180° and that of a complete (whole) angle is 360°.
Solution 4
Let's draw a line that is parallel to the base of the triangle and touches the opposite vertex, as shown in the figure.
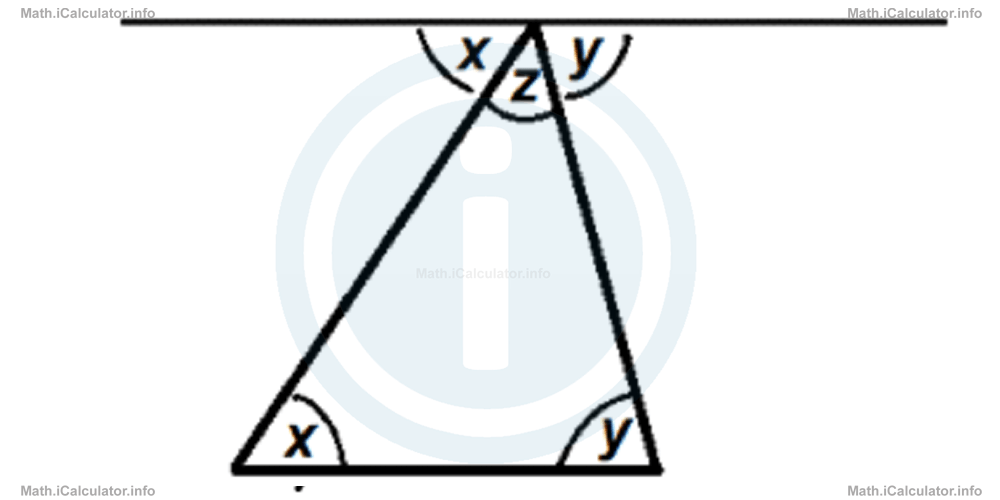
The parallel line allows us obtain two pairs of alternate interior angles, shown by the letters x and y. Therefore, since the three angles on the top part of the figure form a straight angle, we have
Since the angles x and y correspond to the other two interior angles of the triangle, we obtain the same relation for the sum of the interior angles of a triangle as well. Therefore, the initial supposition is proven.
More Identities Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Solving by Proof" math lesson? People who liked the "Identities lesson found the following resources useful:
- Solving By Proof Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this solving by proof (see below)
- Equations Math tutorial: Identities. Read the Identities math tutorial and build your math knowledge of Equations
- Equations Video tutorial: Identities. Watch or listen to the Identities video tutorial, a useful way to help you revise when travelling to and from school/college
- Equations Revision Notes: Identities. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the math tutorial for Identities
- Equations Practice Questions: Identities. Test and improve your knowledge of Identities with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Equations questions with our excellent Equations calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Equations Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning equations - read our next math tutorial: Iterative Methods for Solving Equations
Help others Learning Math just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Math tutorial "Identities" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this math tutorial (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this math learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of math and other disciplines.
Equations Calculators by iCalculator™
- Completing The Square In Quadratics Calculator
- First Order Equations With One Variable Calculator
- First Order Equations With Two Variables Calculator
- Solving Quadratics Through The Quadratic Formula
- Solving Systems Of Linear Equations With The Substituting Method Calculator
- Solving Systems With One Linear And One Quadratic Equation Calculator