Menu
Math Lesson 16.3.7 - Absolute Value Function
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Math lesson on Absolute Value Function, this is the seventh lesson of our suite of math lessons covering the topic of Basic Functions, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional Math learning resources below this lesson.
Absolute Value Function
The absolute value of a number (denoted by two vertical lines aside the number) represents the distance of a number from the origin, no matter in which direction it lies. For example, the absolute value of -3 and + 3 is 3 because both numbers are three units away from the origin.
From the above description, it is clear that the absolute value function f(x) is identical to the corresponding function without the absolute value symbols g(x) only for f(x) ≥ 0, where the two graphs of f(x) and g(x) are identical. The rest of the function f(x) (where without the symbols of absolute value it would normally give a negative output) has a graph that is obtained by mirroring g(x) on the upper part of the coordinates system.
Look at the figure below where the graphs of two functions, f(x) = |x - 2| and g(x) = x - 2 are shown. You can see that for f(x) ≥ 0 the two graphs fit while for f(x) < 0 they become distinct from each other.
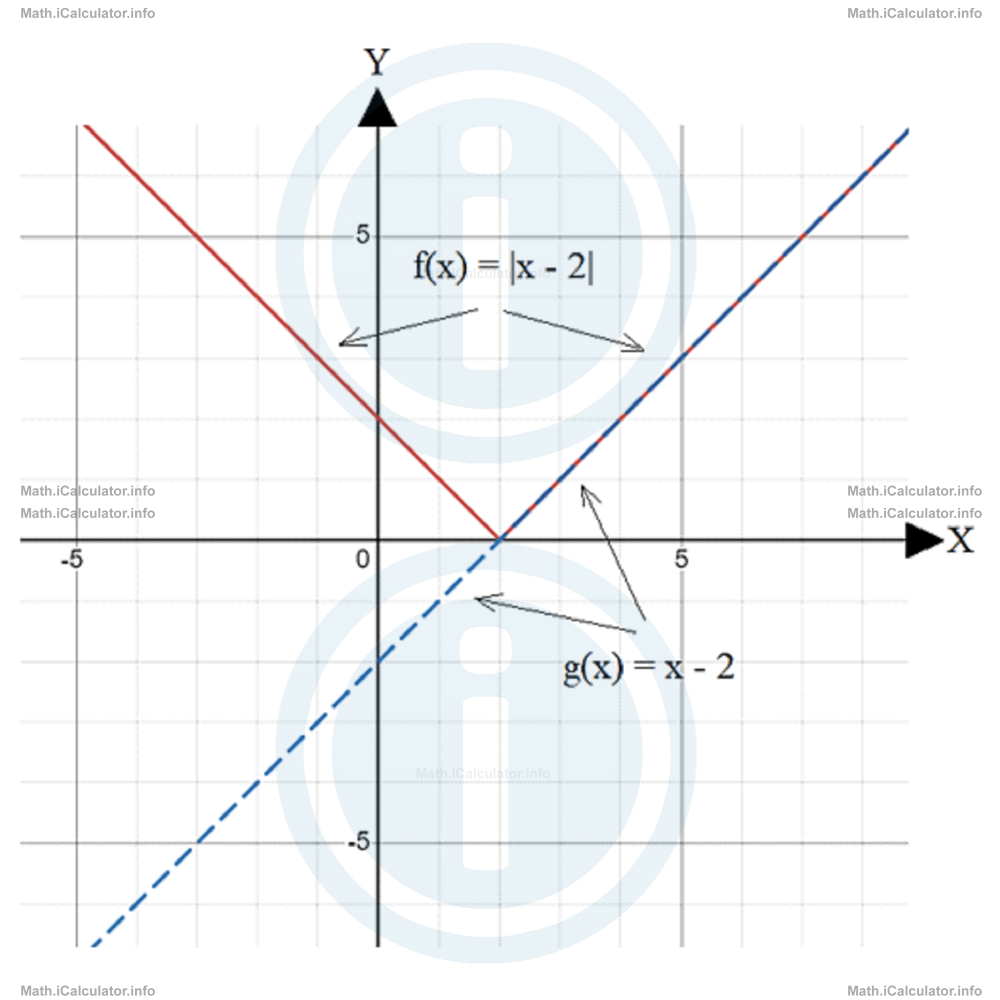
Therefore, despite of the fact that the domain of an absolute value function is not restricted, the restriction occurs at the range, as it cannot be negative.
The absolute value function may contain other types of expressions besides the linear ones. The procedure, however, is the same as described above.
Example 7
For the function
- Find the domain and range
- Plot the graph for x ∊ [-4, 4].
Solution 7
- If there is no restriction in the set of the independent variable x, the domain is the set of real numbers. Hence, we have D = (-∞, + ∞).
As for the range, it is clear that since the expression inside the absolute value cannot be negative, the range of the function f(x) cannot be smaller than -1. Thus, R = [-1, + ∞). - Since the graph must extend between x = -4 and x = 4, the range will be from -1 (the minimum point of the graph) and 11 (the maximum point of the graph) because f(-4) = |(-4)2 - 4| -1and
= |16 - 4| -1
= |12| -1
= 12 - 1
= 11f(4) = |42 - 4| -1Therefore, it is sufficient to take only some positive values from 0 to 4 to plot the graph, as the corresponding negative values will give the same results. Thus,
= |16 - 4| -1
= |12| -1
= 12 - 1
= 11f(0) = |02 - 4| -1Therefore, we obtained the following pairs of points: (-4, 11) and (4, 11); (-3, 4) and (3, 4); (-2, -1) and (2, -1); (-1, 2) and (1, 2). The last point is (0, 3). Inserting all these points in the coordinate system and joining them smoothly yields the following figure:
= |-4| -1
= 4 - 1
= 3
f(-1) = f(1) = |12 - 4| -1
= |-3| -1
= 3 - 1
= 2
f(-2) = f(2) = |22 - 4| -1
= |0| -1
= 0 - 1
= -1
f(-3) = f(3) = |32 - 4| -1
= |5| -1
= 5 - 1
= 4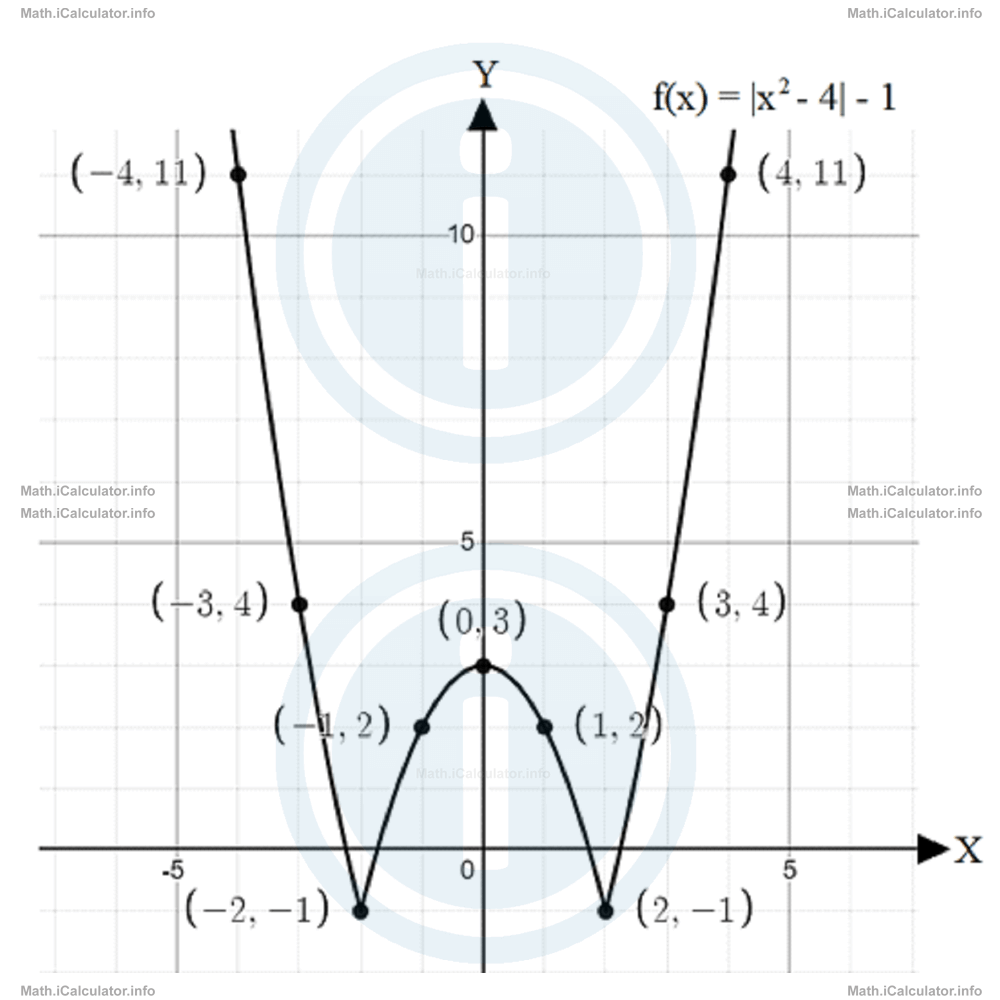
You have reached the end of Math lesson 16.3.7 Absolute Value Function. There are 8 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Basic Functions, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Basic Functions Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Absolute Value Function" math lesson? People who liked the "Basic Functions lesson found the following resources useful:
- Absolute Value Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this absolute value (see below)
- Functions Math tutorial: Basic Functions. Read the Basic Functions math tutorial and build your math knowledge of Functions
- Functions Revision Notes: Basic Functions. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the math tutorial for Basic Functions
- Functions Practice Questions: Basic Functions. Test and improve your knowledge of Basic Functions with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Functions questions with our excellent Functions calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Functions Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning functions - read our next math tutorial: Composite Functions
Help others Learning Math just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Math tutorial "Basic Functions" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this math tutorial (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this math learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of math and other disciplines.