Menu
Math Lesson 16.3.8 - Reciprocal Function
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Math lesson on Reciprocal Function, this is the eighth lesson of our suite of math lessons covering the topic of Basic Functions, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional Math learning resources below this lesson.
Reciprocal Function
The last basic function discussed in this tutorial is the reciprocal function. We have extensively dealt with reciprocal graphs in tutorial 15.4, so we will not dwell too much on reciprocal functions. Just a couple of things are worth to discuss here.
Reciprocal functions have the variable at the denominator of a fraction. It is known that the general formula of reciprocal functions is
where a, h and k are all numbers. The simplest form of a reciprocal function occurs when h = 0, a = 1 and k = 0. This is called the parent reciprocal function and has the form
The graph of reciprocal functions is called a hyperbola. A hyperbola extends in two quadrants and has two asymptotes: one horizontal and one vertical. They represent the limit values of the function.
The following figure shows the graph of the parent reciprocal function, where the two axes act as asymptotes for the graph. Thus, the horizontal axis (y = 0) acts as a horizontal asymptote while the vertical axis (x = 0).
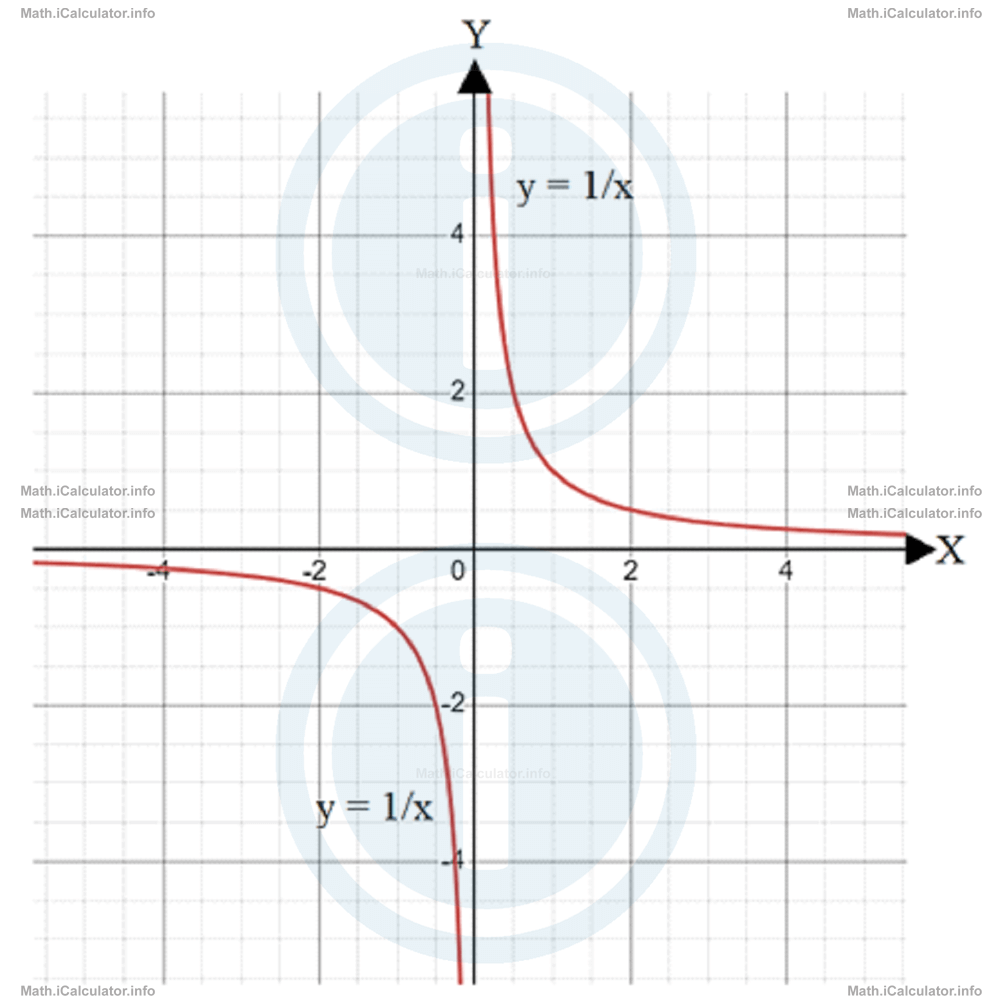
We explained in tutorial 15.4 that the constant h makes the graph shift horizontally by h units while the constant k makes it shift vertically by k units in respect to the reciprocal function y = a/x. The coefficient a instead, makes the graph more distant from the axes when it is greater than 1, although the overall shape of the graph does not change.
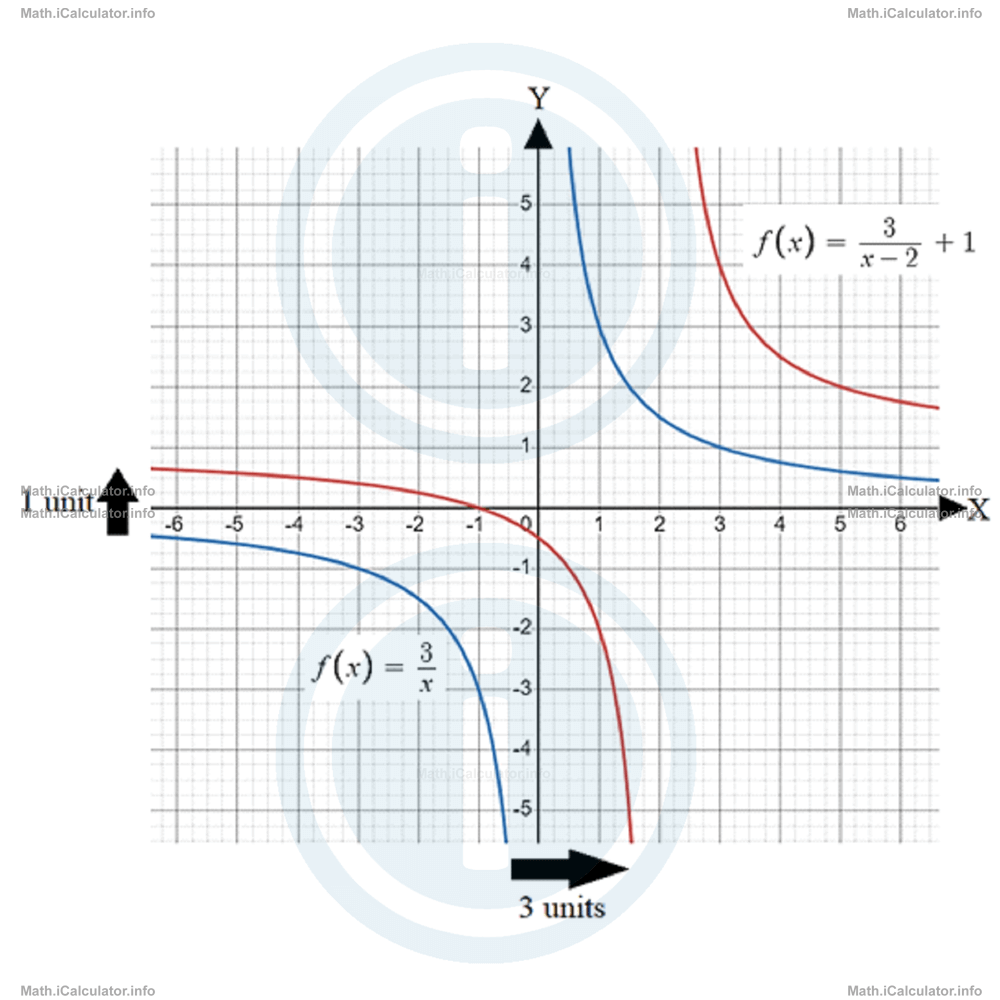
For example, the graph of the reciprocal function
is identical in shape to the graph of
but displaced 2 units on the right and 1 unit above it. Look at the figure below.
The gradient of the parent reciprocal function f(x) = 1/x is
As for the general reciprocal function
its gradient is
The proof for the above formulas will be made in the derivatives chapter.
Example 8
For the function
find:
- Domain and range
- Asymptotes
- Gradient at x = 3
- Equation of the tangent at x = 3
- Plot the graph including the asymptotes and the tangent found at (d).
Solution 8
- There is a restriction in this function: the denominator of the fraction must not be zero. Thus, the domain is obtained for x - 1 ≠ 0 i.e. for x ≠ 1. Hence, we have Domain = Real numbers - {1}. The range includes all the allowed values of f(x). In this case, the allowed values do not include y = 2, as this function is displaced 2 units above the corresponding parent function graph (and 1 unit on the right). Hence, we have Range = Real numbers - {2}.
- Given the results obtained in (a), it is clear that the horizontal asymptote (H.A.) is y = 2, while the vertical asymptote (V.A.) is x = 1.
- We have the following coefficients and constants: a = 4, h = 1 and k = 2. Thus, given the gradient's formula of a reciprocal function m = -a/x - h2we obtain for the gradient m after substitutionsm = -4/(x - 1)2For x = 3, we havem = -4/(3 - 1)2
= -4/22
= -4/4
= -1 - The equation of the tangent line at any point of a function graph is y = mx + nwhere m is the gradient.
The y-value at the point of tangency (x = 3) isf(3) = 4/3 - 1 + 2This allows calculate the constant n of the tangent line. Substituting in the general formula of the tangent, we have
= 4/2 + 2
= 2 + 2
= 44 = (-1) ∙ 3 + nHence, the equation of tangent line at x = 3 is
4 = -3 + n
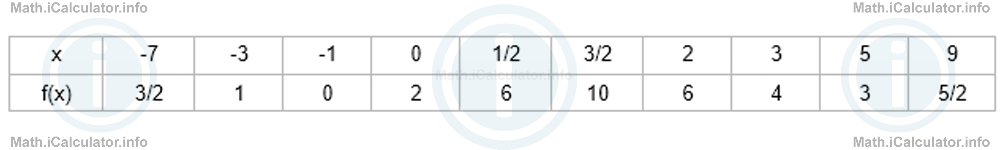
n = 7y = -x + 7where A(3, 4) is the point of tangency. - We can plot the graph by giving some suitable values to the independent variable x and calculate the corresponding y-values. After inserting them on the coordinates system, we join them smoothly. The table with the necessary values is shown below.
 The graph that includes all the above points and the other element found in the other points is shown below.
The graph that includes all the above points and the other element found in the other points is shown below. 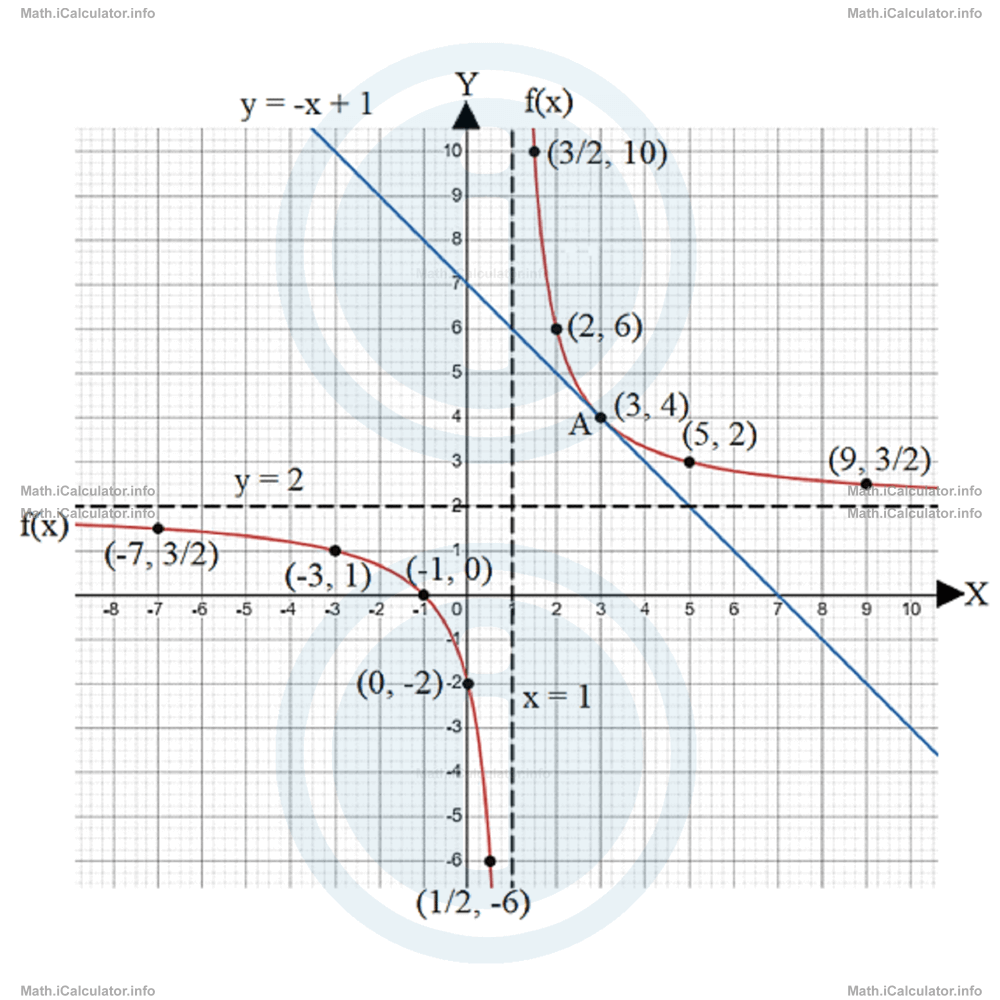
You have reached the end of Math lesson 16.3.8 Reciprocal Function. There are 8 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Basic Functions, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Basic Functions Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Reciprocal Function" math lesson? People who liked the "Basic Functions lesson found the following resources useful:
- Reciprocal Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this reciprocal (see below)
- Functions Math tutorial: Basic Functions. Read the Basic Functions math tutorial and build your math knowledge of Functions
- Functions Revision Notes: Basic Functions. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the math tutorial for Basic Functions
- Functions Practice Questions: Basic Functions. Test and improve your knowledge of Basic Functions with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Functions questions with our excellent Functions calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Functions Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning functions - read our next math tutorial: Composite Functions
Help others Learning Math just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Math tutorial "Basic Functions" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this math tutorial (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this math learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of math and other disciplines.